Switches Aligned, Route Clear! 🚆
It begins with a subtle vibration, deep below the city. Not an earthquake, not a train—at least, not yet. It’s the sound of something carving its way through the ground, silently, methodically, and with surgical precision.
This is the world of Tunnel Boring Machines, or TBMs: giant underground factories that turn rock, soil, and sand into train tunnels, metro lines, and the invisible arteries of modern cities.
You may never see one. But if you’ve ever ridden a subway beneath a historic center, crossed a mountain by train, or stepped into a brand-new metro station in a crowded district—chances are, a TBM made that journey possible.
Machines That Carve Cities
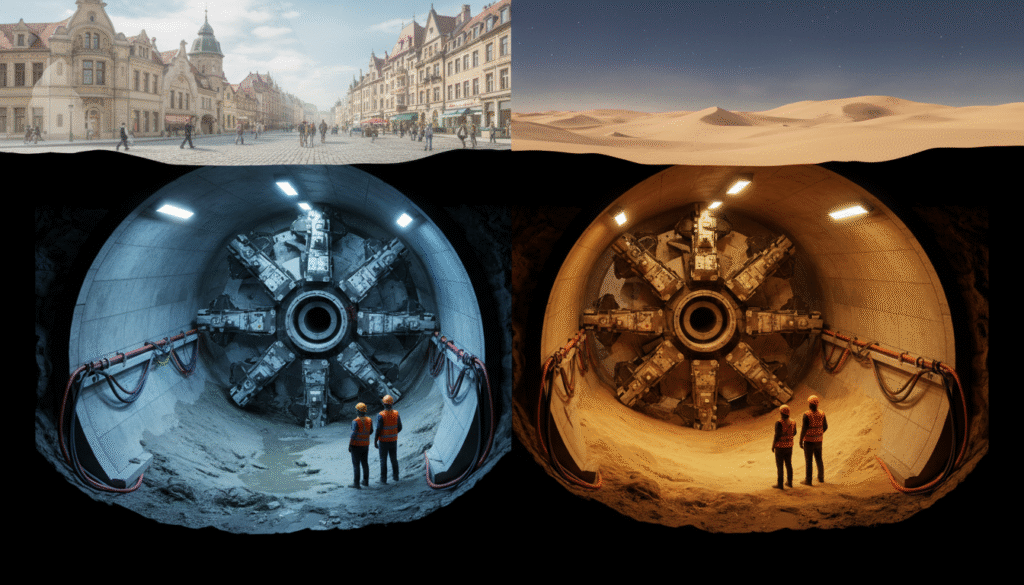
A TBM doesn’t look like a machine. It looks like a monster—100 meters long, with a rotating steel face that eats through the earth.
But what makes it extraordinary isn’t just its size. It’s the way it works: quietly stabilizing the ground around it, removing the spoil, and lining the tunnel with concrete rings—all in one continuous movement. Imagine a mechanical worm, digging and building its own shell as it goes.
Unlike older methods that tear open the streets above, TBMs operate without disrupting what’s on the surface. That’s why they’re the go-to solution in urban environments and under sensitive structures.
Tailoring the Beast to the Ground
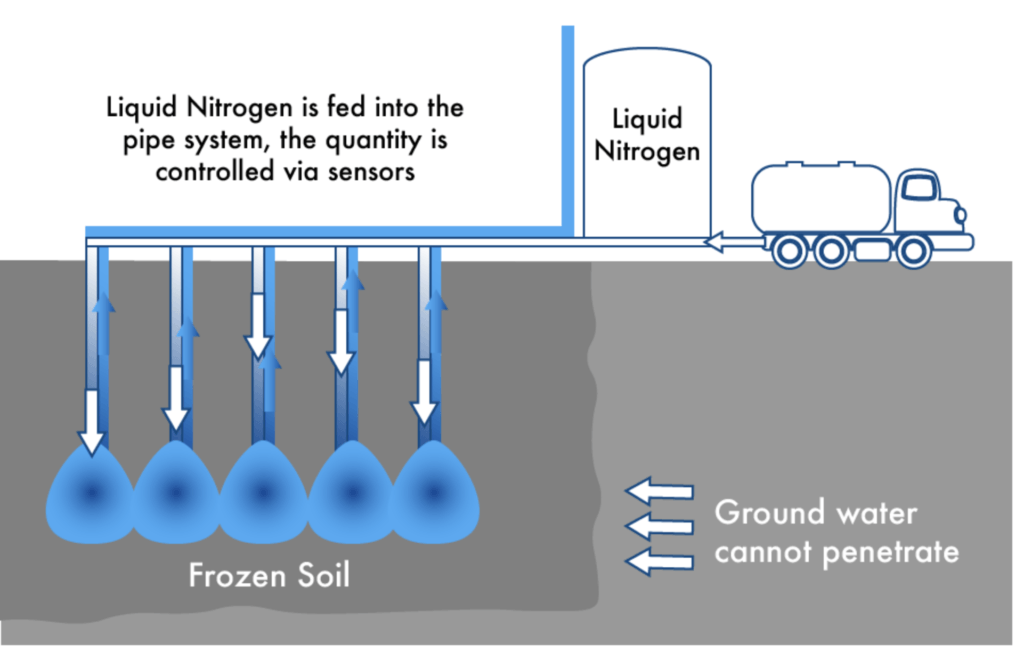
Not all ground is the same. Some soils collapse at the first sign of a void. Others are soaked in groundwater. Some are hard as granite. The beauty of TBMs is that they adapt—each machine is chosen and designed based on the ground it must face.
In soft clay or sandy soil? You’d likely use an Earth Pressure Balance (EPB) machine, which maintains pressure at the tunnel face to keep everything stable.
In loose, water-bearing soils? A Slurry TBM is ideal, pumping pressurized fluid ahead of the cutterhead to hold the earth in place.
For solid rock? A Hard Rock TBM powers through with heavy-duty cutters, grinding stone into dust.
Each TBM is a tailor-made solution, not a one-size-fits-all tool.
Inside the Heart of a TBM
Step inside a TBM—if you ever could—and you’d find a hidden world. Up front, the rotating cutterhead is the star: a massive steel disc studded with tools that chew through ground. Just behind it, a robotic arm installs pre-cast concrete segments to line the tunnel.
Further back, you’d walk through a series of support modules: ventilation, slurry pumps (if needed), power generators, crew cabins, control rooms. It’s a mobile underground factory that breathes, thinks, and adapts.
From the outside, you might see only a control screen or a ventilation pipe. But underground, dozens of people are working in real time to guide this machine forward—literally building the future one meter at a time.
A Global Force Beneath Our Feet
These machines have already left their mark on the world:
-
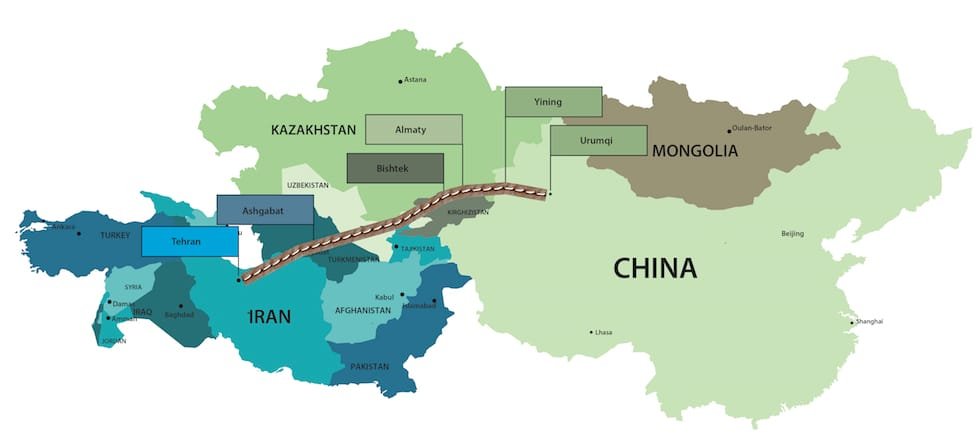
In London, TBMs tunneled beneath centuries-old buildings for the Crossrail project.
-
In Paris, they’re creating an entirely new metro network with the Grand Paris Express.
-
In Switzerland, they bored through the Alps to create the Gotthard Base Tunnel—the longest rail tunnel on Earth.
-
In Milan, they quietly shaped Lines 4 and 5 beneath some of Italy’s most fragile architecture.
Each project faced different ground conditions, different risks, and different demands. But they all had one thing in common: the TBM.
Why TBMs Matter
TBMs aren’t just machines. They’re enablers. They make it possible to build where other methods would fail—or would cost too much, take too long, or disturb too many lives.
They’re safer, too. Workers aren’t exposed to collapsing walls or dangerous blasts. And the surface above—homes, schools, ancient churches—stays untouched.
Still, they’re not magic. TBMs are complex and expensive. They require months of planning, constant monitoring, and an army of specialists. A minor change in geology can halt progress for days. Wear on the cutter tools must be anticipated. And once they start, there’s no turning back.
What’s Next for TBMs?
Like everything else in rail, TBMs are going digital. Machines are now equipped with sensors that monitor pressure, temperature, cutter wear, and more. Engineers above ground watch live dashboards and receive alerts before a problem appears.
AI-assisted control systems are beginning to help operators make decisions faster. Designs are evolving, too—toward cleaner energy, better recycling of materials, and modular assembly for faster deployment.
In the future, TBMs may be smarter, greener, and even more autonomous—but they’ll still be doing the same essential job: creating space where none existed before.
Conclusion: The Art of Building Underground
You don’t have to be an engineer to appreciate a TBM. You just have to ride a train through a tunnel and think: Someone built this. Somehow. And more likely than not, a TBM was the one that did it.
From mountains to metropolises, these machines are quietly shaping the world beneath us—one rotation at a time.
Let us know in the comments or on social media: What part of tunnel construction would you like to explore next? In future posts, we’ll dive into the world of slurry systems, segment lining, and how engineers steer a machine they can’t see.
Stay with Beyond Tracks as we continue to uncover the technologies behind tomorrow’s railways.