When we think of trains, we picture rails, engines, and stations. But behind the scenes, one of the most important elements is invisible: communication.
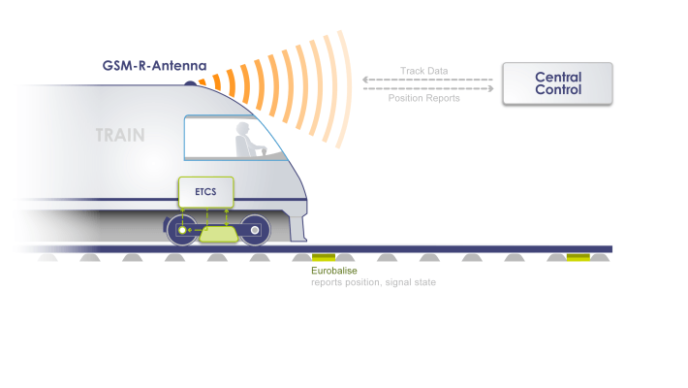
Without it, trains wouldn’t know when to stop or go, drivers couldn’t reach control centers, and systems like automatic signaling or real-time traffic updates wouldn’t function. At the heart of this silent but essential world lies GSM-R — the Global System for Mobile Communications – Railway.
Used across much of Europe and Asia, GSM-R is a technology designed specifically for the railway industry. It’s not your everyday mobile phone network. It’s smarter, more robust, and deeply integrated into how modern railways operate safely and efficiently.
Why GSM-R Matters
GSM-R was developed as an evolution of the GSM mobile standard, but tailored to meet the needs of rail operators. That means full coverage along tracks — including tunnels and remote sections — and communication that doesn’t drop, even when trains are traveling at 300 km/h.
One of its key roles is to support ERTMS (European Rail Traffic Management System), particularly Level 2 and Level 3, where traditional trackside signals are replaced by continuous communication between the train and the control center. Without GSM-R, that real-time flow of instructions — the core of modern train safety — wouldn’t be possible.
It also allows for special types of calls like group calls, emergency broadcasts, and functional addressing (calling “Train 457” rather than a phone number), which are essential when seconds matter during disruptions or incidents.
Where It’s Used
Today, GSM-R is operational across most of Europe — including Germany, France, Spain, and Italy — and it’s deeply embedded in projects where ERTMS is being deployed. It is also the system of choice in China, which operates the world’s largest high-speed rail network.
The system is being phased in — or considered — in several other countries as part of their railway modernization plans, including parts of Africa, the Middle East, and India.
But while GSM-R has transformed railway communication over the past two decades, it’s now approaching the end of its lifecycle.
What Comes Next: The FRMCS Transition
The future is FRMCS — the Future Railway Mobile Communication System — currently being developed under the guidance of the International Union of Railways (UIC) and 3GPP, the international body behind mobile communication standards like 4G and 5G.
Unlike GSM-R, FRMCS is designed from the ground up as a 5G-native system. It promises higher bandwidth, lower latency, and better support for new applications like video streaming from onboard cameras, real-time diagnostics, and predictive maintenance powered by AI.
Trials are already underway in several countries — including France (SNCF), Germany (DB Netz), and Finland — with a coordinated transition expected between 2026 and 2035, depending on national timelines and regulatory approvals.
Challenges Ahead
Moving from GSM-R to FRMCS won’t be immediate. The two systems will coexist for years, especially on international corridors. This means infrastructure must support interoperability, and rail operators must be trained to manage both platforms.
Another critical issue is cybersecurity. As more railway systems become connected, they also become more vulnerable to digital attacks. That’s why FRMCS is being developed with strong encryption, authentication, and secure network segmentation from the outset.
Conclusion: The Network You Never See
GSM-R may not be visible to passengers, but it’s part of what makes modern railways function. It has kept trains safe, schedules on time, and rail traffic flowing across borders.
As we move toward the next generation of railway communications, GSM-R’s legacy will remain — not just as a technical platform, but as the system that helped railways transition into the digital age.
At Beyond Tracks, we’ll continue to explore how these unseen technologies shape the journeys of tomorrow.
Verified Sources and Technical References
International Union of Railways (UIC): https://uic.org
→ FRMCS Programme and GSM-R Standards DocumentationEuropean Union Agency for Railways (ERA): https://www.era.europa.eu
→ ERTMS Implementation and GSM-R Deployment Reports3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project): https://www.3gpp.org
→ Release 17/18 – FRMCS SpecificationsUIC ERTMS & GSM-R Handbook – 2021 Edition
→ Comprehensive technical guide for European rail telecom standardsDB Netz / SNCF / Trafikverket press releases (2022–2024)
→ FRMCS testing programs and migration strategiesRailway Gazette International / IRJ / Global Railway Review
→ Industry reporting on FRMCS trials, GSM-R limitations, and transition planning